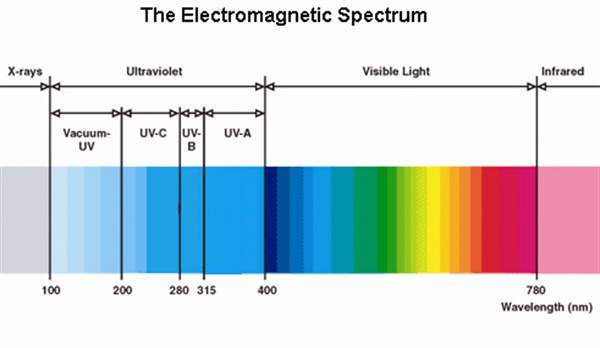
 Ultraviolet radiation forms part of the light spectrum. It is classified into three parts.
Ultraviolet radiation forms part of the light spectrum. It is classified into three parts.
UV-C (Short Wave) from 100 Nanometers to 280nm
UV-B (Medium Wave) from 280nm to 315nm
UV-A (Long Wave) from 315nm to 400nm
Ultraviolet radiation is invisible to our eyes. UV lamps do produce visible light but this does not have any effect on the performance of the lamp.
UV-C is germicidal i.e. the radiation emitted deactivates the DNA of bacteria, viruses and other pathogens and therefore destroys their ability to multiply and cause disease.
The UV germicidal radiation (254nm) actually causes damage to the nucleic acid of microorganisms by forming covalent bonds between certain adjacent bases in the DNA. The formation of such bonds prevent the DNA from being unzipped for replication and so the organism is unable to reproduce. In fact when the organism tries to replicate it dies.
Ultraviolet technology is a non-chemical approach to disinfection. Nothing is added which makes this process simple, inexpensive and requires very low maintenance. Ultra violet purifiers utilize germicidal lamps that are designed and calculated to produce sufficient dosage of ultraviolet radiation to deactivate the bacteria.
 The most efficient source for generating UVC is the low-pressure mercury discharge lamp, where on average 35% of input watts is converted to UVC watts. The radiation is generated almost exclusively at 254 nm a.
The most efficient source for generating UVC is the low-pressure mercury discharge lamp, where on average 35% of input watts is converted to UVC watts. The radiation is generated almost exclusively at 254 nm a.
Most low pressure tubular fluorescent ultraviolet lamps have an envelope of special glass that filters out ozone-forming radiation, in this case the 185 nm mercury line.
A second type of UV source is the medium pressure mercury lamp, here the higher pressure excites more energy levels producing more spectral lines and a continuum (recombined radiation) should be noted that the quartz envelope transmits below 240 nm so ozone can be formed from air.
The advantages of medium pressure sources are:
Micro-organisms effective resistance to UV light varies considerably. Moreover, the environment of the particular micro-organism greatly influences the radiation dose needed for its destruction.
Water, for instance may absorb a part of the effective radiation depending on the concentration of contaminants in it. Iron salts in salts in solution are well known inhibitors. Iron ions absorb the UV light.

UV lamps contain small amounts of mercury ( less than 0.1%), which is a toxic and therefore hazardous substance, hence any used UV lamps have to be recycled/disposed of in a safe manner and separately from normal household waste in order to optimise re-use and recycling.
The disposal of UV lamps must comply with the Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE) directive and the HSE guidelines.
If you require your lamps to be disposed, please contact your nearest recycling centre, or to a supplier/retailer with a lamp disposal programme like the one offered by CLS-UV, which is a Recolight programme.